Hackers primarily target gambling due to the profitable financial opportunities it offers. The online gambling industry is a fertile ground for malicious actors seeking to exploit vulnerabilities for financial gain and data theft.
Cybersecurity analysts from ASEC recently discovered that threat actors have been actively distributing the infamous WrnRAT, disguising it as gambling games.
ASEC recently uncovered a sophisticated malware operation in which malicious actors created deceptive websites offering popular Korean gambling games such as “badugi,” “two-player go-stop,” and “hold’em” to distribute malicious software.
WrnRAT Delivered in the Form of Gambling Games
When users download what appears to be a game launcher, the system initiates a multi-stage infection process, in which a batch script (containing comments in Korean) is executed first, followed by a .NET-based malware dropper (distributed under filenames such as “Installer2.exe”, “Installer3.exe”, and “installerABAB.exe”). This dropper installs and executes the main malicious payload known as “WrnRAT.”
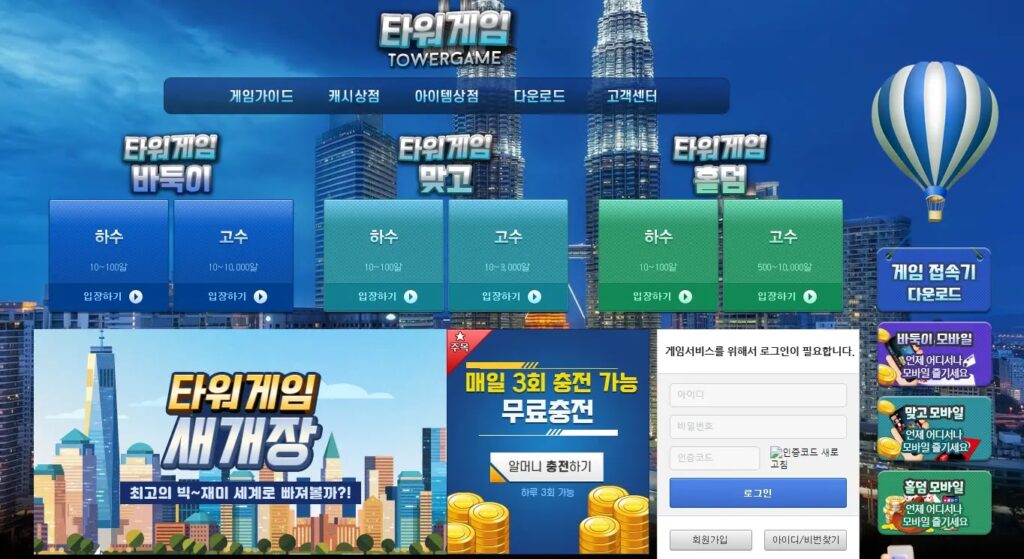
Deceptive page for downloading gambling games (Source – ASEC)
This dropper operates by creating both a launcher component and the actual WrnRAT malware, executing WrnRAT through the launcher, and then self-destructing to evade detection.
In the final stage, WrnRAT installs itself on the system, disguising itself as “Internet Explorer” by creating a file named “iexplorer.exe” to blend in with legitimate system processes.
The malware was also distributed through HFS platforms, sometimes posing as computer optimization software, demonstrating the attackers’ varied distribution strategies.
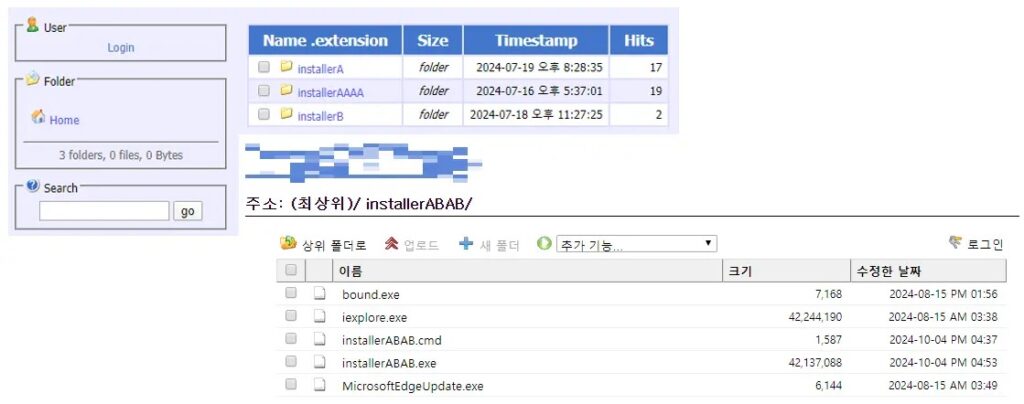
Platforms used for malware distribution (Source – ASEC)
Once successfully installed, WrnRAT provides attackers with remote control over the infected system and allows them to steal sensitive information from the compromised machine.
WrnRAT is a sophisticated malware developed using the Python programming language and packaged into an executable file using PyInstaller.
This RAT primarily operates by capturing and transmitting screenshots from infected computers to the attacker’s system.
Moreover, it collects essential system information and has the capability to terminate certain active processes.
The malware authors have expanded their toolkit by developing additional tools that modify firewall configurations to evade detection.
The primary motivation of these malicious actors appears to be financial exploitation.
They monitor users’ games through unauthorized screenshots, leading to significant financial losses, especially for users accessing illegal gambling platforms.
By observing players' hands, betting patterns, and strategies in real time using the screenshot capture functionality, attackers can gain unfair advantages or steal sensitive information.
Preventive Measures
Here are some essential preventive measures:
- Download software only from official stores or verified sources.
- Ensure that you have a robust antivirus solution in place.
- Keep your device up to date with the latest security updates.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) (IoCs)
MD5
0159b9367f0d0061287120f97ee55513
03896b657e434eb685e94c9a0df231a4
0725f072bcd9ca44a54a39dcec3b75d7
0d9e94a43117a087d456521abd7ebc03
1b8dfc3f131aaf091ba074a6e4f8bbe6
Suspicious URLs:
http[:]//112[.]187[.]111[.]83[:]5723/installerABAB/MicrosoftEdgeUpdate[.]exe
http[:]//112[.]187[.]111[.]83[:]5723/installerABAB/bound[.]exe
http[:]//112[.]187[.]111[.]83[:]5723/installerABAB/iexplore[.]exe
http[:]//112[.]187[.]111[.]83[:]5723/installerABAB/installerABAB[.]cmd
http[:]//112[.]187[.]111[.]83[:]5723/installerABAB/installerABAB[.]exe
Suspicious FQDN Domains:
aaba1[.]kro[.]kr
delete1[.]kro[.]kr
inddio23[.]kro[.]kr
nt89kro[.]kr
nt89s[.]kro[.]kr
Original article Notorious WrnRAT Delivered Mimic As Gambling Games published by Cyber Security News.
